The CI/CD pipeline is one of the best practices for DevOps teams to implement, for delivering code changes more frequently and reliably.
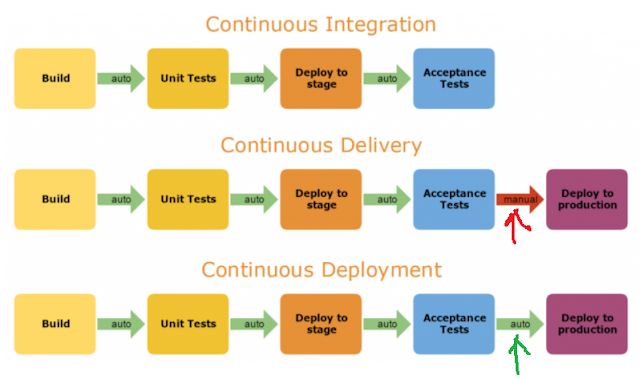
Continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) embody a culture, set of operating principles, and collection of practices that enable application development teams to deliver code changes more frequently and reliably. The implementation is also known as the CI/CD pipeline.
CI/CD is one of the best practices for DevOps teams to implement. It is also an agile methodology best practice, as it enables software development teams to focus on meeting business requirements, code quality, and security because deployment steps are automated.
CI / CD defined
Continuous Integration is a coding philosophy and set of practices that drive development teams to implement small changes and check in code to version control repositories frequently. Because most modern applications require developing code in different platforms and tools, the team needs a mechanism to integrate and validate its changes.
The technical goal of CI is to establish a consistent and automated way to build, package, and test applications. With consistency in the integration process in place, teams are more likely to commit code changes more frequently, which leads to better collaboration and software quality.
Continuous delivery picks up where continuous integration ends. CD automates the delivery of applications to selected infrastructure environments. Most teams work with multiple environments other than the production, such as development and testing environments, and CD ensures there is an automated way to push code changes to them.
CI/CD tools help store the environment-specific parameters that must be packaged with each delivery. CI/CD automation then performs any necessary service calls to web servers, databases, and other services that may need to be restarted or follow other procedures when applications are deployed.
Continuous integration and continuous delivery require Continuous Testing because the objective is to deliver quality applications and code to users. Continuous testing is often implemented as a set of automated regression, performance, and other tests that are executed in the CI/CD pipeline.
For more info please go through the url below
https://dzone.com/articles/secure-and-scalable-cicd-pipeline-with-aws
https://eduinpro.com/blog/top-devops-tools-in-the-digital-market/